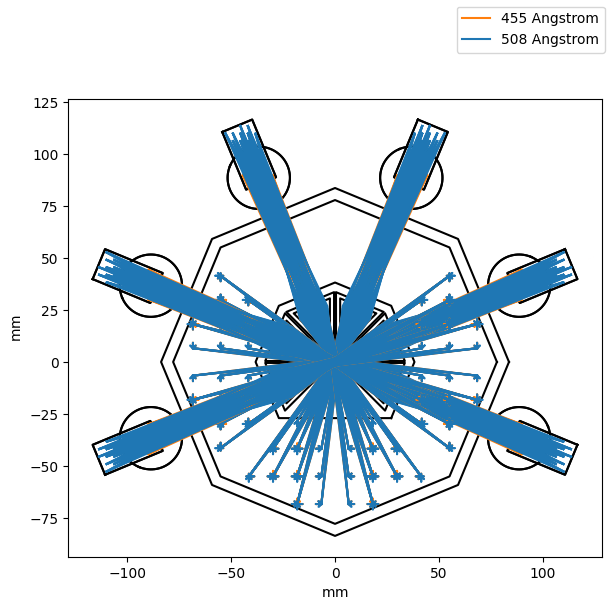
design_proposed#
- esis.flights.f2.optics.models.design_proposed(grid=None, num_distribution=11)#
Final optical design for ESIS 2.
- Parameters:
grid (None | ObjectVectorArray) – sampling of wavelength, field, and pupil positions that will be used to characterize the optical system.
num_distribution (int) – number of Monte Carlo samples to draw when computing uncertainties
- Return type:
Examples
Plot the rays traveling through the optical system, as viewed from the front.
import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import astropy.units as u import astropy.visualization import named_arrays as na import optika import esis grid = optika.vectors.ObjectVectorArray( wavelength=na.linspace(-1, 1, axis="wavelength", num=2) / 2, field=0.99 * na.Cartesian2dVectorLinearSpace( start=-1, stop=1, axis=na.Cartesian2dVectorArray("field_x", "field_y"), num=5, ), pupil=na.Cartesian2dVectorLinearSpace( start=-1, stop=1, axis=na.Cartesian2dVectorArray("pupil_x", "pupil_y"), num=5, ), ) model = esis.flights.f2.optics.models.design_proposed( grid=grid, num_distribution=0, ) with astropy.visualization.quantity_support(): fig, ax = plt.subplots( figsize=(6, 6.5), constrained_layout=True ) ax.set_aspect("equal") model.system.plot( components=("x", "y"), color="black", kwargs_rays=dict( color=na.ScalarArray(np.array(["tab:orange", "tab:blue"]), axes="wavelength"), label=model.system.grid_input.wavelength.astype(int), ), ); handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels() labels = dict(zip(labels, handles)) fig.legend(labels.values(), labels.keys());